No products in the cart.
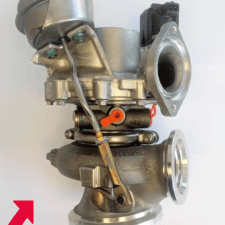
Upgraded Journal Bearings
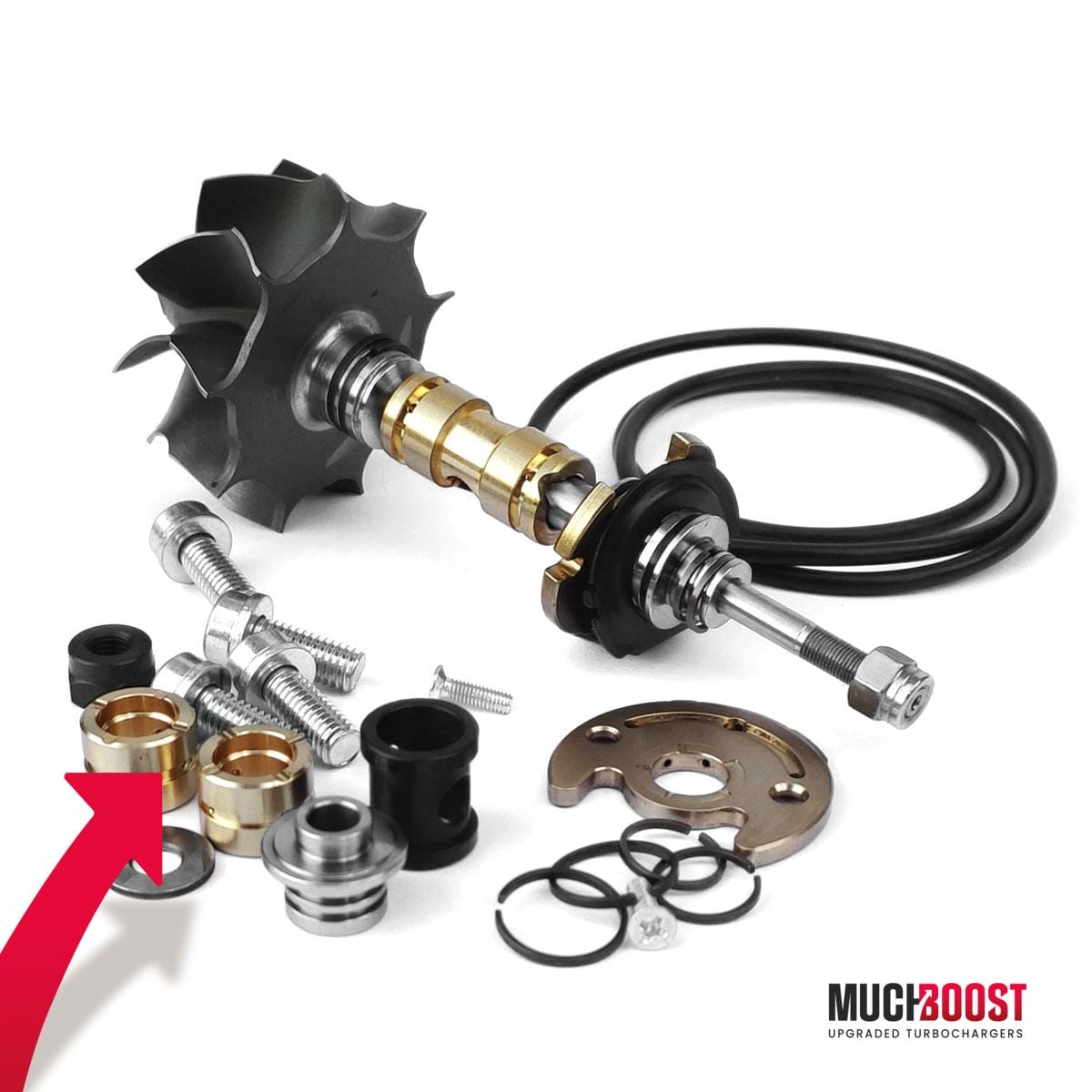

Bearings are one of the most important components when building the turbo. They are responsible for the ease of spinning and even wear. The bearings are what allow the turbo to spool up to 100 000 RPM.
Turbocharger bearings are a vital yet sometimes overlooked component of the turbocharger. A correctly designed bearing system can be the difference between a turbocharger that runs efficiently and effectively for the duration of the engine’s life and one that has durability issues. In the face of rising pressure to lower engine fuel consumption and emissions, turbocharger-bearing systems are likewise changing. Higher turbocharger efficiency is frequently demanded by newer engines, which can often be partially achieved by minimizing bearing system losses.
Bearings must be able to tolerate:
High thrust loading. Significant thrust loads can be created by high boost pressure acting on the compressor wheel. Due to a VGT’s capacity to drive the compressor to higher boost pressures at low flows, the thrust loading in variable geometry turbines can be even higher. Low flow in the VGT usually indicates a small nozzle setting and low static pressure acting on the turbine wheel, both of which are insufficient to appreciably counteract the compressor thrust.
Oil contaminants. Longer periods between oil changes may lead to oil being contaminated and they can cause the bearing surfaces to rust.
Delayed oil supply. The longer it takes for the oil to lubricate the turbo the more likely “dry” bearings are to wear unevenly or too fast.
Not cooling down after a ride. A turbo needs to cool after a long or intense drive. Shutting the car down right after stopping, with no idling time, may cause localized overheating issues and cause damage to the bearings.
Reduced bearing friction can play a crucial role in improving cold start emissions and fuel economy in an era of rising pressure to minimize emissions and fuel consumption. Additionally, as engine oil viscosities decrease, either due to the usage of low viscosity oils or due to fuel dilution during post injections for DPF regeneration, turbocharger bearing systems must adjust to maintain rotor-dynamic stability and avoid increasing wear.
There are two types of modern commercial turbocharger bearing systems: hydrodynamic journal bearing systems and ball bearing systems. Hybrid systems combining journal and ball bearings are also possible.
At MuchBoost.com, we very often opt for upgraded journal bearings to improve the longevity of our products and give you the best price-to-performance ratio, although some ball-bearing turbos are also available.
Why are upgraded bearings better?
The bearings we use (so-called 360-degree bearings) allow for running higher boost pressures. Also, the bigger surface area is stronger and can handle more serious axial loads. Thanks to a bigger number of oil pipelines, lubrication is vastly improved compared to a standard bearings system.

-
 1.6JTDM/Multijet Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo MiTo, Fiat 500L, Bravo II, Grande Punto, Punto EVO, Idea, Lancia Delta III, Musa I949,00 € – 1039,00 €
1.6JTDM/Multijet Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo MiTo, Fiat 500L, Bravo II, Grande Punto, Punto EVO, Idea, Lancia Delta III, Musa I949,00 € – 1039,00 € -
 1.3 Multijet Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo MiTo 1.3JTDM, Fiat Doblo, Grande Punto, Idea, Linea, Lancia Musa, Ypsilon1099,00 €
1.3 Multijet Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo MiTo 1.3JTDM, Fiat Doblo, Grande Punto, Idea, Linea, Lancia Musa, Ypsilon1099,00 € -
 1.5 VGT Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo Tonale 48V1999,00 €
1.5 VGT Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo Tonale 48V1999,00 € -
 2.4 JTDM Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo 159, Brera, Spider, Fiat Croma II1099,00 € – 1299,00 €
2.4 JTDM Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo 159, Brera, Spider, Fiat Croma II1099,00 € – 1299,00 € -
 Alfa Romeo 2.0T De-Cat/Sport Cat 100CPSI Downpipe for Alfa Romeo Giulia, Stelvio899,00 € – 1249,00 €
Alfa Romeo 2.0T De-Cat/Sport Cat 100CPSI Downpipe for Alfa Romeo Giulia, Stelvio899,00 € – 1249,00 € -
 1750/1.8 TBi Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo 159, Giulietta, Lancia Delta III 1.8 DI T-Jet1799,00 € – 1999,00 €
1750/1.8 TBi Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo 159, Giulietta, Lancia Delta III 1.8 DI T-Jet1799,00 € – 1999,00 € -
 2.2D Multijet II Alfa Romeo Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo Giulia, Stelvio1599,00 €
2.2D Multijet II Alfa Romeo Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Alfa Romeo Giulia, Stelvio1599,00 € -
 N74 6.0/6.6 V12 Hybrid Twin Turbo Upgrade Rolls-Royce Ghost, BMW 760i F01/F02/F031949,11 € – 8129,11 €
N74 6.0/6.6 V12 Hybrid Twin Turbo Upgrade Rolls-Royce Ghost, BMW 760i F01/F02/F031949,11 € – 8129,11 € -
 1.4 TB/T-Jet Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Fiat 500 Abarth 595, Grande Punto, Alfa Romeo Giulietta, MiTo1105,77 € – 1474,77 €
1.4 TB/T-Jet Hybrid Turbo Upgrade Fiat 500 Abarth 595, Grande Punto, Alfa Romeo Giulietta, MiTo1105,77 € – 1474,77 €